The debt explosion: How neoliberalism fuels debt crises
Political economists Radhika Desai and Michael Hudson discuss the massive explosion of debt in the US and around the world, and how neoliberal economics leads to large bubbles based on speculation.
Political economists Radhika Desai and Michael Hudson discuss the massive explosion of debt in the US and around the world, and how neoliberal economics leads to large bubbles based on speculation and asset-price inflation.
You can find more episodes of Geopolitical Economy Hour here.
Video
Podcast
Transcript
RADHIKA DESAI: Hello and welcome to the 21st Geopolitical Economy Hour, the show that examines the fast-changing political and geopolitical economy of our time. Welcome also to a new year that promises to be nothing but rocky, so let's help rock it in the right direction. I'm Radhika Desai.
MICHAEL HUDSON: And I'm Michael Hudson.
RADHIKA DESAI: There's an old saying, money makes the world go around. Like so many other truths, neoliberalism has subtly but decisively altered this one too. The adage of the neoliberal age can be said to be "debt makes the world go around".
Indeed, debt is not just making the world go around, it is making it spin madly. So madly that the possibility that it will spin out of control is ever present.
Everywhere you look, there's a debt crisis. There's a student debt crisis, the mortgage crisis of 2008 never really went away, there's the commercial real estate crisis, there's a government debt crisis, and of course, there is the crisis of housing, I mean credit card debt, auto debt, etc.
To keep the debt cycle going, the Federal Reserve is even changing its decade-long tolerance of intolerance of inflation. For the Federal Reserve, inflation is acceptable at 3.5%, according to some reports. It would rather tolerate 3.5% inflation than sacrifice the asset markets that keep going up thanks to which have kept going up thanks to low interest rates, and it doesn't want to take interest rates beyond a certain level.
Raising interest rates at this point means making it harder for asset markets to go up and stay up, and that's why the Federal Reserve is going to cut interest rates no matter whether it's managed to solve the inflation problem or not.
So today, we are going to continue our closer look at more than four decades of neoliberal policy and how they've changed our economy by focusing on the triangle of debt, real estate, and financial instability.
In short, we are going to talk about how in these decades while incomes have stagnated, debt has expanded such that households, governments, and businesses have all become indebted to the gills.
Today, one of the reports shows that debt servicing itself has gone up by 50% and today accounts for almost a sixth of total government spending in the United States.
How both residential and commercial real estate have become bound up in the vortex of financialization is another thing we want to talk about because it is not producers but rentiers who benefit from this type of economy, and even rent is being converted by the alchemy of financialization into interest.
So at the end of the day, even land ownership and home ownership no longer matter. What matters is how much money you've got and how you can make your money make more money.
So finally, we are going to talk about how even though all of this has benefited the financial sector, given its very nature, the expansion of the financial sector can only lead to crisis, and so how the mountain of debt today threatens the stability of the US financial sector and by turn of the US economy, and as Michael and I have discussed so many times, the dollar system itself.
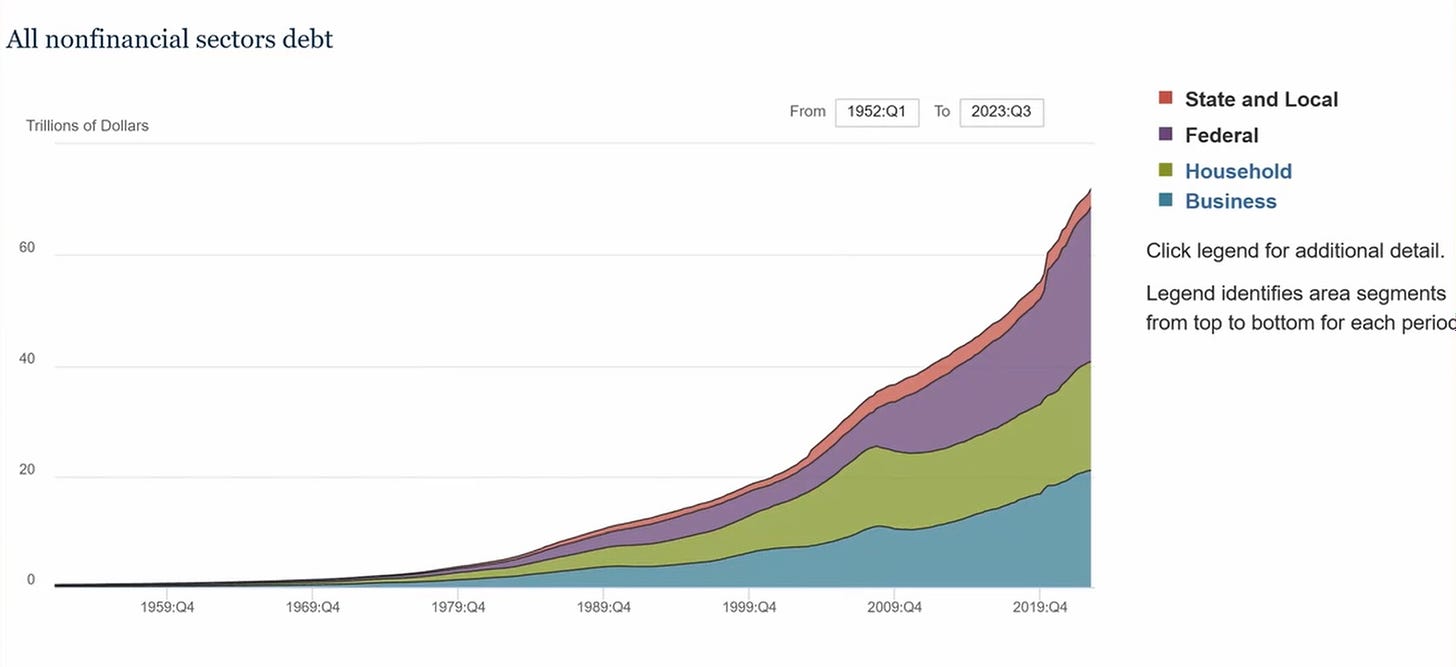
So let's start looking at this chart. This is the chart of total indebtedness in the United States.
So you see here, this is simply the aggregate level of indebtedness. The kind of blue bits at the bottom are business debt, this green bit here is household debt, this purple bit here is federal debt, and then on top, you have state and local government debt which of course as people will know has been restricted by constitutional, by legal means.
So what you have here is debt from the 1960s onwards, and you can see clearly that really the debt, the accumulation of debt begins to take off only out in the neoliberal era from the 1980s onwards, and it really begins to take off around the 2000s when of course the United States Federal Reserve first experimented with low-interest policies, and of course, which then resumed after the 2008 financial crisis.
MICHAEL HUDSON: Well, you can look at the basic sweep which is an up sweep, an exponential growth. Any debt is a doubling time, and there's something very unique about this kind of slope. The economy doesn't grow like that, the economy grows in business cycles, up and down.
What you don't see here is very much of a downswing, and that is because the growth of debt continues to mount up by compound interest. The creditors, the banks, simply reinvest all of the interest that they get in making new loans, which is exponential, and they can create their own money simply on their own computers.
So, this chart really should be juxtaposed with one of the business cycles, then you'll see that any debt that grows this rapidly exceeds the ability to be paid, and that is the distinguishing feature of debt for the last 5,000 years. The natural tendency of debt is to exceed the ability to be paid.
Now, this chart simply shows debt by the sector that owns it, the household sector, business. What it does not indicate is what this debt is for. What is it collateralized for? Well, almost all of the household debt is for real estate, and the same thing with commercial bank debt. 80% of bank loans for this debt are real estate loans.
And the blue chart of government debt really doesn't matter that much because the government simply creates the debt. And it's debt that doesn't ever expect to be repaid. Households and businesses have to pay the debt. That's what's causing the problem. Nobody ever got into trouble running into debt.
The government doesn't run into trouble running into debt because it can simply print the money to pay. But individuals, families, and corporations have to pay. And when they can't pay, that hurts the banks, and the banks go under.
And the purpose of the Federal Reserve is to make sure that this debt keeps on growing despite the fact that it is stifling the economy and leading to depression.
The role of the central bank is to impose austerity on the whole rest of the economy to make us look like a Third World country in paying the debt, because this is exactly the same kind of sweep that you have for the global south countries owing their foreign debt and for every country in the west.
So the whole West, Europe, the United States, has a chart just exactly like this, and they're all slowing down, and they're all in what's called a debt deflation right now.
RADHIKA DESAI: Well, you know, I'd just like to add a few more points because this chart is really kind of more interesting than might appear at first sight. Of course, there is the upsweep that you talk about, Michael, but there is also the fact that if you look at the period from essentially from about 1950 till the end of the 1970s, there is an upsweep, but it is not so pronounced.
What you see now in the neoliberal era after 1980, and particularly after about 2000, that's when you see the really exponential increase in debt. And I think that that, as I say, coincides with two very important things.
Number one, the repeal of the Glass-Steagall Act, which meant that this was essentially permission for the U.S. financial sector to simply enter into the most breakneck competition with one another in order to lend more and more, speculate more and more, and so on. So that's what you're looking at.
And of course, the other part is the historic decision after the 2000 crash, the dot-com bubble crash, when the Federal Reserve first began experimenting with low interest rates.
So you had sort of one, between one and two percent interest rates from about 2000 till about 2004-5, when because the dollar was coming under a lot of pressure, the Federal Reserve was forced to start raising interest rates. And that graduated series of interest rate increases was, of course, what eventually pricked the housing and credit bubble. So, I mean, that's one thing.
The second thing as well is that United States government debt as well. You know, at one level you can say that, yeah, sure, the government debt doesn't have to be paid off. But the thing is, it's not as though the government debt does not matter.
At the end of the day, even when the U.S. government, or when even the U.S. government borrows a lot, it does suffer. Because today, the U.S. government is having to pay much more money in return for its debt in order to borrow from the market than it used to have to.
So, and even in the era of low interest rates, U.S. government paid a higher premium, higher interest rates on its debt than, say, a country like Germany, for example.
So in that sense, I think that what you see here, which is particularly after the increase in the debt in the neoliberal era, this initial increase here you see up to 2008, is basically created out of essentially giving tax cuts to rich people. So that expanded the federal deficit, even though you had cutbacks in Social Security and so on.
And today, a very large part of U.S. debt is actually going to paying interest rates, paying interest on U.S. government debt. So in that sense, it's important.
And then finally, of course, the expansion of household debt, which again, you see it increases, it increased a little bit in the 1980s, then it sort of slowed, but then you see it particularly increasing in the 2000s with the housing and credit bubble.
Then it slows again, and then once again, it is increasing. And this increase, of course, is almost entirely because of the difficulties in which U.S. households find themselves.
So on the one hand, at the top end of the borrowing, of course, you have borrowing in order to consume more, in order to spend more in one or the other way, including in order to speculate more in stock markets. But on the other hand, you also have a lot of distressed borrowing. So this is what we are looking at.
And finally, this increase in business debt is also because essentially what has been happening over the last several decades is that companies are bought by other companies.
And then what these companies do is they burden every business they buy with as much debt as they can get in order to essentially use the money for other purposes, including giving fat dividends to owners and so on.
But this is what you're looking at. So we're looking at a highly, highly indebted world.
MICHAEL HUDSON: Well, there are a number of points also in that chart. After 2000, a lot of that government debt was the war debt, the Iraq War debt. From 1950 through about 1980, almost all the growth in government debt was military spending abroad.
And this debt is not only owed to the United States holders and the Federal Reserve, but the foreign government. So that is not included in the chart, but that's much of the growth.
The interesting thing also is that you see this acceleration of debt after 2008, and yet that was the period of zero interest rate policy.
When the Obama crash occurred, the Federal Reserve said, the one thing we have to make sure is that families bear the brunt of this enormous financial fraud and bad lending and junk mortgages that have taken place. We want to save the banks and we want to sacrifice homeowners for it. We want to make the public pay to the banks to make sure that homeowners lose their home and lose money.
Businesses go bankrupt, but the banks continue to get richer and richer with this debt, and this debt will not get wiped out by bankruptcy. It's going to grow and grow, just like student loan debt has grown. And you see a lot of this business debt going up, and yet this business debt was almost interest free, very low.
What the chart should be correlated with, if we really had a group of charts, was all of this debt was spent not on producing goods and services, not in building factories and means of production, not in employing labor, but in buying stocks and bonds and speculating. It was all used to buy companies, load them down with debt.
And so this corporate debt that's going up is a result of the mergers and acquisitions, the corporate raids, the corporate takeovers, and treating corporations in a way that would make money for their stockholders and their private owners, but not for the economy at large.
So a company would make money, suppose you take over Sears or Toys R Us, the private capital that would take over, they would borrow the money, hardly any interest from a bank, 100%, buy out Sears or another company.
The first thing they'd do is say, okay, now we've taken over the company, could be the Chicago Tribune, let's take the pension funds that's invested in stocks and let's borrow against that. Let's let the pension funds lend the money to the company, and let's borrow more money from the banks to the company. And the money that we borrow, we will then pay out a special dividend to ourselves.
So the money goes from the banks to the owners without having any positive effect at all, but having a very negative effect. It leaves the company so deeply in debt that it goes bankrupt, like Sears or Toys R Us or all of the other companies that have been essentially going bankrupt.
And when they go bankrupt, they're sold to larger and larger companies. And so this debt has the effect of concentrating ownership within the sector.
And the household debt has gone up because as you increase the amount of money that banks will lend against housing, banks have competed. Who can lend the most money against homes for new families wanting to buy a home?
Well, the banks compete to lend so much money that if you're a family buying a home, you have to borrow more money than your rival who's borrowing from their bank, and the banks have just created a new real estate bubble.
And that's what we're in now. The real estate prices have gone up so high, the rental price is so high that one of the byproducts of this is a rise in homelessness.
And with all of this debt, somehow people don't have enough money to buy goods and services, and standards of living have gone down.
We're living in a increasing Third World austerity plan as a result of this upsweep in debt.
RADHIKA DESAI: No, absolutely. And you know, what you say reminds me that we've already said that one of the reasons why especially poor households borrow is because they basically cannot make ends meet. They have to borrow, and so they are becoming indebted.
But there's another reason, and that is, you know, why has there in the neoliberal decades been such a huge explosion in student debt? It's because government cutbacks have stopped funding universities to the same extent. So fees go up.
And of course, the cost of living goes up for students because of course you can't rent anything half decent, or even indecent, unless you pay a lot of money. And so all of these things drive up the cost of an education, which then means that students have to get a loan, and so on.
So essentially, cutbacks in social services, including, by the way, we haven't talked about medical debt. A lot of the debt is incurred because people have to borrow money if they want to pay for certain medical procedures.
So all of these things just goes to show that once again, under neoliberalism, it's ordinary people, the working people, and the poor people who get really shafted.
There's another way in which these people get shafted. When you have a low interest rate fueled competition for buying houses, buying homes, typically the sharpest competition is happening at the lower end of the market.
So that the lower end market, that is to say the kind of houses and homes that first time buyers will buy, tend to see the most appreciation in prices as a result of competition among the lower end buyers. And this is what prices out so many people.
But a final thing I want to say is this expansion of debt is also interesting because it has taken place exactly in that era when the government, right at the beginning of the 1980s, committed itself to restricting money supply, it committed the Federal Reserve to restricting money supply in order to slay the dragon of inflation.
But what that has meant essentially is to have an economy in which people are making less money but incurring more debt. And essentially debt becomes the way in which money is issued into the economy.
And of course the Federal Reserve itself has kept up a policy going back to 1987 where no amount of money creation is too much if it is to bail out the financial sector. So from 1987 onwards, when you had the 1987 crash, Greenspan first engaged in this kind of liquidity provision in order to bail out the financial sector. It was called the “Greenspan put”.
Now over the years it has become a Federal Reserve put. And the result is, you know, we just showed you the chart of indebtedness. And according to the Federal Reserve, the total debt or non-financial debt in the United States is now close to three times U.S. GDP. It has doubled since 1980.
There is another point that is really interesting. These charts, the chart we showed you, does not include the vast amount of debt which the Federal Reserve has itself created in order to bail out the financial sector. And the top end of the corporate sector, starting in 2020, on which the financial sector relies for its best assets.
So essentially, and this was very surprising to me, in 2008, a scholar called James Fulkerson from your university, Michael, from UMKC (University of Missouri-Kansas City), showed that the Federal Reserve could not cope with the 2008 crisis by just playing its normal role of lender of last resort, by providing ample liquidity, slashing interest rates, etc. It slashed interest rates at that time from 5% to 0%. But this did not function to stabilize the system and even made it worse.
And then, according to Falkerson, the Federal Reserve engaged in a host of unconventional measures, unprecedented in terms of size or scope and of questionable legality. They're his words. And the goal of these was to explicitly improve market conditions. And this program, according to him, amounted to a total of 29 trillion dollars.
MICHAEL HUDSON: You've gone very quickly over that, and I want to show how revolutionary this was. Until from the founding of the Federal Reserve to 2008, there was a basic philosophy of central banks going all the way back to the Bank of England and to the rules that people discussed in the 1880s and 1890s.
The idea of central banks, you used the words “lender of last resort”. That means everybody realized that sometimes when there would be a business downturn or a shift in interest rates, people would have very sound property. The buildings weren't destroyed when they became insolvent. Companies weren't destroyed.
But the problem is there was a temporary downturn in the business cycle. So banks are supposed to only borrow for short term and at a high penalty rate. Every central bank in the world followed the policy. You don't subsidize rates for credit for banks.
Since 2008, the banks have taken control of the U.S. Treasury and taken control of the Federal Reserve to get all the money that they want for nothing. Actually, they're paid to borrow.
After 2008, the Fed said, we've got to make bankers richer. Despite the fact that they're paying themselves more than any other sector, they don't have enough money to keep on lending. We will give them all the money they want. The way we'll do this is the banks will make loans to corporations for takeovers, make loans for commercial real estate. They will transfer these IOUs to the Federal Reserve in deposits.
The Federal Reserve will lend them money in exchange for this. The banks have put all of their bad loans and shaky loans into the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve pays them interest on these deposits. The banks make interest not from the corporate borrowers, but the Federal Reserve is creating the interest to pay the banks to make this huge upsweep in loans.
You can look at that as an arm of Chase Manhattan and Citibank. Essentially, they've taken control of the Federal Reserve.
That's really the libertarian ideal of a centrally planned economy planned by the banks. When the libertarians say, let's get the governments out of business, let's get the governments [to not] run a deficit, that means if the government doesn't run a deficit, it'll cut taxes, it'll cut spending. That means that all the credit that people need, the economy needs, will be produced by the banks.
The Fed has said, now we're going to really turn up the screws. We're going to let the banks make 5% of the money. All of a sudden, this growth in the blue, the government debt that you saw, is going to soar. The interest rates are going to be such a large proportion of the government spending that they're already talking about, we're going to have to cut back Social Security and Medicare.
That's what [Nikki] Haley, the Republican nominee, says. The Republicans want to say, if there's a choice between paying Social Security and Medicare or paying interest to the banks and bondholders, the bondholders come first because they're our campaign contributors. You don't get campaign contributors from people who are broke because they don't have the money that the banks have. Of course, we're going to bail out our campaign contributors.
The government itself has been privatized. That's what neoliberalism is. That's what the anti-government libertarianism is. It means liberty for the banks and debt system for the population at large. That's what these charts imply.
RADHIKA DESAI: Absolutely. I would say just one thing. Of course, most people will know this, but in case people don't, the Federal Reserve is peculiar among the central banks of the world in being still privately owned. In that sense, I think that what Michael says is very relevant.
Essentially, what the Federal Reserve has done is over the last many decades, it has transformed the U.S. economy into an economy in which the primary way, the best way, the fastest way to make money is by essentially speculating, not by investing in the production of goods and services that ordinary people need, but by inflating the value of goods and services already produced.
Those of you who know a little bit of Marxism might appreciate it, but if Marx was around, he would have called it a very peculiar form of necromancy. What do I mean by that? Because already produced goods and services contain the dead labor that has gone, it is now dead, it is no longer living, that has gone into producing it and you are inflating the value of that.
Whereas, as you do that, you are disvaluing the living labor, much of which may remain unemployed, and all of which is necessary to produce the new goods and services which every year, in every period, ordinary people need.
We need more food, we need more clothing, we need more transportation, we need more housing, etc., etc. And these are the things that are strangulated. Living labor is strangulated while dead labor goes up. Because there's something very peculiar.
Remember, as Michael pointed out, and as I pointed out, a lot of this debt has been incurred. In fact, most of it has been incurred to speculate, to inflate the value of already existing assets. And there's something very peculiar about it, because imagine a house that goes up in price by 30%, 40%, 50%. Nothing in it may have changed, but it goes up in price anyway. Nothing is produced, but it goes up in price. So, this is the kind of economy that has been created.
And I just also want to show you one other outcome, just my last point this time around, but one other outcome of this vast increase, this vast federal government program to bail out the financial institutions.
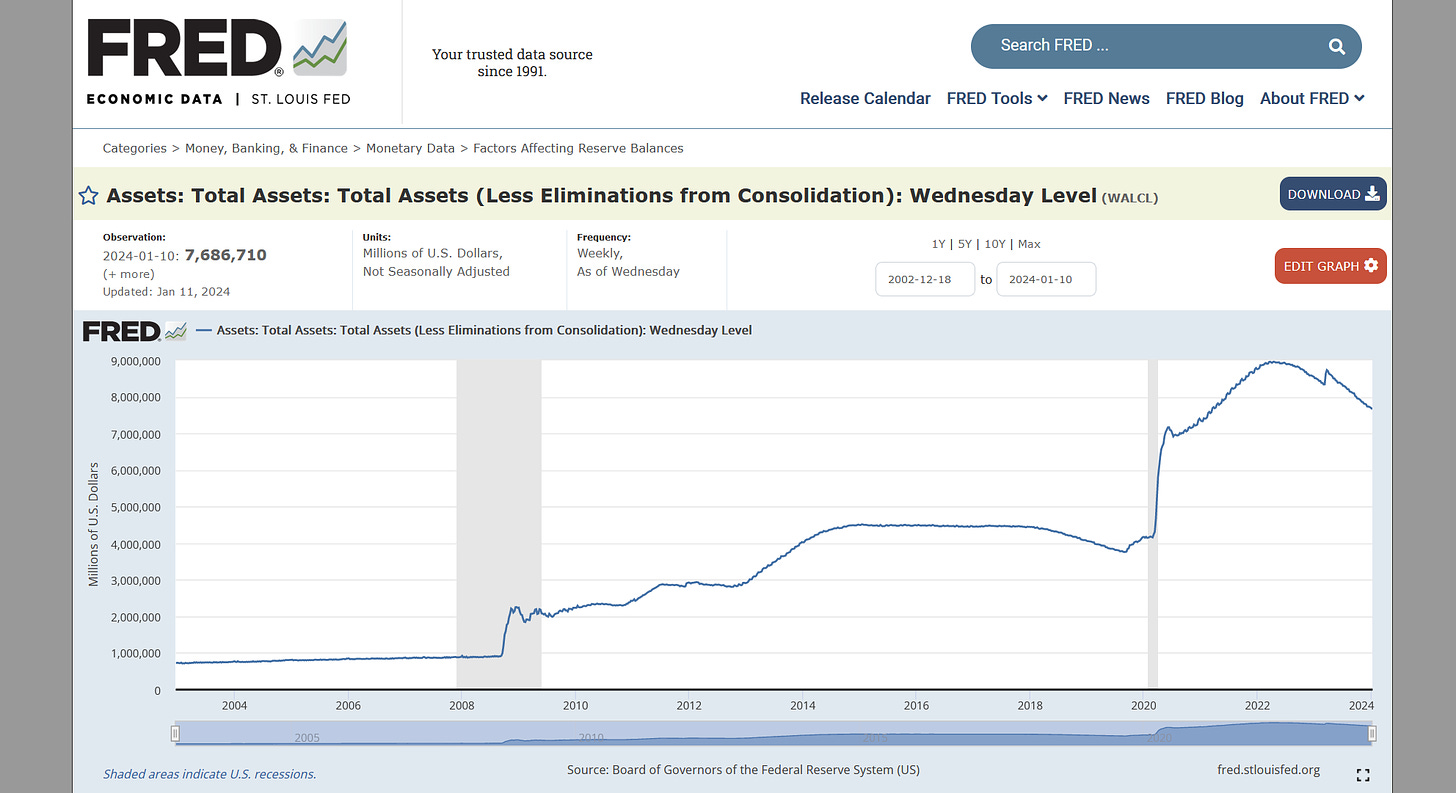
So, you see here, this is a chart of the total assets on the Federal Reserve balance sheet.
And you see here, from up until the 2000s, it was basically hovering at about just below $1 trillion. In the 2008 financial crisis, it doubled, a little more than doubled actually, to over $2 trillion.
Then over the course of the decade that followed, thanks to quantitative easing in which the federal government essentially started a program to buy the worthless assets of the financial institutions for good money. This was quantitative easing, and so it piled on, it increased its own balance sheet while essentially making good the damaged balance sheets of the very financial institutions that had caused the 2008 financial crisis.
And then it was beginning to reduce its balance sheet when 2020 came, the pandemic came, and then you see that you have seen an absolutely unprecedented increase to $9 trillion of assets in the federal government. And this is the result of that $29 trillion worth of effort that the Federal Reserve made to bail out the financial sector.
So, please, Michael, go ahead, yeah.
MICHAEL HUDSON: When you use the [phrase] "worthless assets", they weren't exactly worthless if you could get 100% from the Federal Reserve. The word that was used by Marx and almost everyone in the 19th century and today was "fictitious capital". In other words, all of these debts and bank assets were counted as an asset.
If a bank makes a loan to a large corporate property owner in an office building, the bank has that as an asset. But as we're seeing today, these asset prices can't be realized. In other words, what if the bank said, okay, now your mortgage is just falling due because it's a balloon mortgage, you have to pay that. Every few years, you have to pay the entire amount or re-borrow it.
Well, all of a sudden, if it's lent $100 million against an office building, and the office building is now worth $40 million, why would a bank lend $100 million to an owner of a $40 million office building? That's the situation we're in today.
Now, look at these two jumps. The first jump that you have after 2008, that's the junk mortgage jump. All of these loans were against fictitious mortgages, mortgages that pretended that there was value there, but there were mortgages mainly to Black and Hispanic borrowers by banks who cheated them, who over-evaluated the prices.
The banks in general discovered a new way of making money after about 2004. They could make money by charging racial minorities much higher rates, almost double the rates that they charged white people. There were whole banks and brokers that specialized in this, and this was basically the junk mortgage group. Countrywide, Financial was the most obvious beneficiary of this.
There were a number of notorious banks that ended up being merged. Bank of America was one of the crooked banks. Citibank was one of the most crooked banks, as has been very well documented.
Randall Wray at the Levy Institute and Kansas City published a big explanation of who were these $29 trillion, $27 trillion of loans for. It ended up many of these loans were rolled over and reloaned, so the net amount was not $27 trillion, but that's how much was given to the banks with this huge jump. Instead of sending the bankers to jail, they made them billionaires. They rewarded them.
That was the Obama policy, and that is what makes them one of the most viciously racist presidents in modern American history. The Democratic Party became committed to returning to its pre-Civil War racist policies.
Well, the next group is you see in 2020-21, this huge jump in bank loans. What were they from? The Federal Reserve began to raise interest rates. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates from less than 1% to 5%, this means all of a sudden debtors had to pay 10 times as much interest as they did before.
What that did was that reduces the price of an asset. It's an inverse proportion to the interest rate. All of a sudden, the stocks and the bonds held by the banks that went under were fictitious.
In fact, although Silicon Valley Bank and New York Bank went under, all of the banks, especially Citibank and Chase Manhattan, had all of the loans that they had. All of a sudden, they were not worth anywhere near what they carried them on the books. The banks were insolvent.
Now, here was a wonderful opportunity. The Federal Reserve could have taken them over by the government and said, you're insolvent. We're going to wipe out the stockholders and the bondholders because you've made bad loans. Instead, the Federal Reserve said, well, instead of making the banks insolvent, let's make the economy insolvent.
That's the policy we're in today. This increase in Federal Reserve loans has been to support this upsweep of credit that is increasing the burden. All of this upsweep in credit is far in advance of the wages and salaries that people are getting.
Somehow, all this increase in interest charges and amortization charges and penalty fees end up impoverishing the economy by leaving less to spend on food and clothing and other consumer spending. If consumer spending is going up, it's because of the inflation.
RADHIKA DESAI: A small correction. This big increase, of course, was increased because the Federal Reserve started a new, massive liquidity provision program, quantitative easing program, when the pandemic hit. And the one that you're talking about, where essentially they were bailing out Silicon Valley Bank, etc., this is the small increase here, which is what happened after interest rates started rising. But throughout this period, right up until about here, interest rates remained at historic lows.
And just one other thing I wanted to say about this before we close this chat, which is that, you know, around 2013, about here, essentially, the Federal Reserve decided that it was going to try to decrease the size of its balance sheet.
So you can see, you know, it was still only about three and a half trillion, not the nine trillion that it is today. But you know what the financial institutions and the financial sector did? The financial sector at the time, in 2013, threw a "taper tantrum".
The Federal Reserve was threatening to taper its balance sheets essentially, you know, to decrease it. And they said, we're not having it. You've got to keep supporting us and you've got to buy our assets. And so essentially, the Federal Reserve humored them in their tantrum and they continued to expand the balance sheet. And then, as we saw in the pandemic, did even more so, etc. So that's the thing we're looking at.
And the other thing I just wanted to point out, of course, is that, you know, I completely agree with everything that Michael said about just how racist the system is, because at the end of the day, you know, people think that debt is a market relationship.
Debt is not a market relationship. It's a relationship between, on the whole, relatively privileged people, one of which decides to lend money to the other. So the idea that somehow, by passing a piece of legislation, you can make the poor people of the United States, the black people of the United States, the Hispanic people of the United States into homeowners, this was always a bit problematic.
And in the end, the whole 2008 financial crisis, the vast buildup of debt that preceded it, only a tiny fraction, which happened towards the very end of that vast increase, was actually loans to subprime borrowers. The financial institutions only began lending to the subprime borrowers once they had filled the prime borrowers to the gills with all the debt they could take, and only then they moved.
And so, in many ways, the subprime borrowers came last, and they were also, of course, the ones to suffer the most. So, yeah, I mean, I think these are really, so really we are living in an economy that is awash with debt, as we were just saying, and it really is the opposite of the sort of economy we ought to have.
And Michael, you know, one of the things about the whole classical conceptions of land and rent and interest and so on is, of course, that classical political economy always looked down on things like this, like interest and rent, because it saw it as unearned income, isn't it?
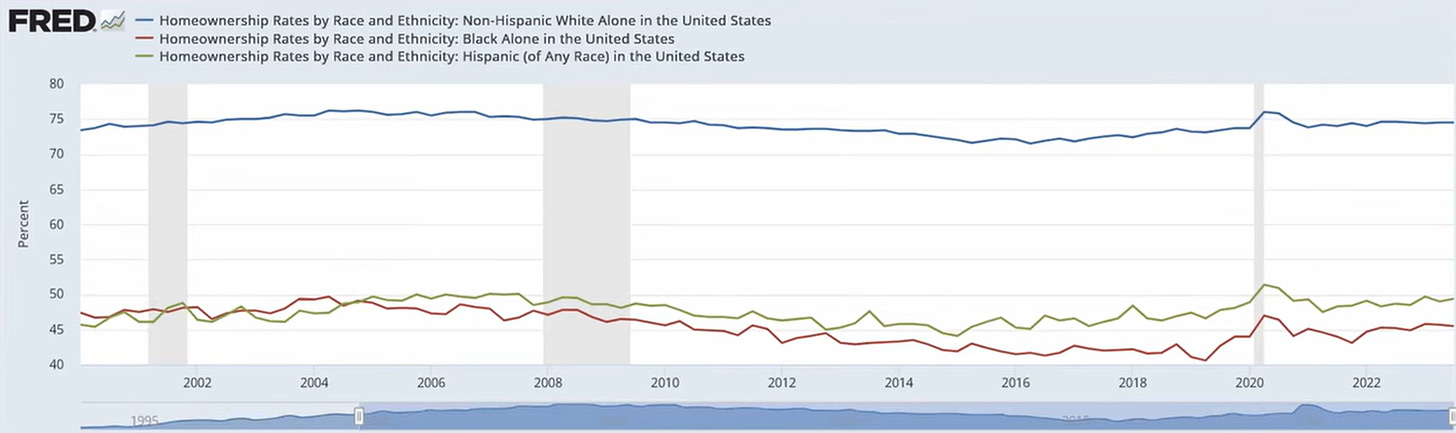
MICHAEL HUDSON: Well, I could have a whole hour on that, but I want to follow up with some charts on the racial element of this. We've talked about how the volume of debt is too large to be paid, but I want to say there's another aspect of debt, and if you could show the racial, that's right, that chart is very interesting.
One of the results of debt is to create a bifurcated economy, and that means that we're in a kind of apartheid economy. We're in a financial apartheid economy. 10% of the population owns over 75% of the stocks and bonds in the population, and they're almost entirely a white population.
We've talked about mortgage debt being 80% of the overall debt burden. I want to show what has happened long before the chart begins in 2002.
I want to begin in 1945 at the end of World War II. That's really when the houses had not been built during the Depression because people, there wasn't a market for them. They weren't being built during World War II because all of the raw materials were going to the war effort, and debt for the whole economy was very, very low debt in 1945 because there was nothing to borrow money for. You couldn't borrow money to consume because everything was rationed anyway.
But finally, they began to make loans, and what had spurred the American takeoff and that of other countries. All countries of Europe, America, and elsewhere were rebuilding after the war, and most of this rebuilding was rebuilding for housing. That was when the great housing was taking place. Here in Queens, you had major developers, not only Trump's father, but all the famous experiments and group housing were made.
There was only one thing. White people were able to buy houses for maybe $10,000 was a typical price of a house that now costs a million dollars. The problem is that banks would only, in order to buy a house, you had to take out a mortgage. Nobody has enough money to buy the whole value of a house, and if wages were maybe $3,000 or $4,000 a year back in 1945, you couldn't even buy a $10,000 house. Nobody had that. You had to go to the banks. Banks, until about 2000, 2001, would only make mortgage loans almost entirely to white people, unless you were a very, very wealthy black person or a Hispanic.
What you created was a bifurcated society. The people who bought the houses in 1945—they returned from the war. They took civilian jobs. They bought a house, and many of them died of old age, but they left the houses to the children.
And you had one generation after another generation of white people leaving the house to the children, leaving them enough inheritance to have a house of their own and an education of their own. So what you had was a home-owning, educated white class, but this was not available to non-whites in this country.
So what's the depth of the restriction of credit to the prime human beings, not to the unprimed borrowers? We're talking about a pretty racist policy. It was very responsible for the fact that you've had now 75 years—well, longer than that, 75 years since World War II—you have a disenfranchised, non-white class in the United States of hereditary homeowners who can get into college because their parents and grandparents went to an Ivy League university.
And there's a monopoly of housing and education and wealth at the top of the economic pyramid, and the rest of the economy is essentially disenfranchised as if we're in our own financialized apartheid economy.
RADHIKA DESAI: Yes, and there's a couple of other points. By the way, in this chart, I should just explain that the top line here is essentially showing the home ownership rates, that is about 75 percent, of non-Hispanic whites in the United States.
The red line, which is at the bottom here, is of black people alone in the United States, and then the green line is of Hispanics of any race in the United States. So that presumably includes, for example, if you were a relatively white Hispanic, and they do a little bit better.
But you can see that the rate of ownership of black people from the early 2000s till today has really not budged. If anything, it's slightly worse today than it used to be back then, and became considerably worse just before the pandemic, reaching a very low level of below, like around 40 percent, in fact. So anyway, that's the thing.
But in addition to these things, the kind of financialized economy in which we live, increasingly owning of houses and land, etc., does not necessarily, because of mortgages, the ownership of land or houses does not necessarily confer on you any privilege, because homeowners find that they are paying interest to banks, and even landlords typically are highly leveraged, so the bulk of what they are collecting in rent actually ends up as interest to banks.
So in a certain sense, what we are trying to say is that the Federal Reserve has engineered an economy in which not only profits and wages have become essentially in hock to pay interest, are used to pay interest, but so is rent. So that interest has become sort of the prime form of income, at the top of the income pyramid, so to speak.
And this is a result of changes also in the tax structure. So for example, in the U.S. taxation system, earnings from interest and rent are treated a lot more softly, a lot more favorably than our earnings from work. This is a huge problem.
MICHAEL HUDSON: That sort of goes back to the value theory that I think requires a separate discussion altogether, because it's so fundamental.
The whole idea of classical economics and the free market was a market to be free from rent, rent being unearned income. Rent is what landlords make in their sleep.
Rent is not created by labor, and most people don't realize what's called the labor theory of value that is based on Ricardo and Marx and the whole 19th century.
The idea was to separate value, which is created by labor, from economic rent, which is created by hereditary, by privilege, by property ownership, by owner, by banking, and by monopolists, and by landlords who make their money, economic rent, by owning a rental property, or by lending money and making interest, or by having a company, a monopoly.
And you just raise prices, and much of the inflation, as Radhika mentioned at the beginning of the talk, they call it profit inflation, meaning a company just decides, let's raise the price of drugs.
For instance, my wife is on an employer, United Healthcare plan. The price that she has to pay, local drugstores went up quintupled on January 1st, because the healthcare insurer said, we can make money by quintupling the price.
Drug companies have been raising the prices all across the board, not by producing more, not because their costs have gone up, which would be, ultimately, the cost would be a cost of production, labor, and materials, but simply because they've become a monopoly.
And the Democratic Party has always been the great protector of monopolies, because they're campaign contributors. And if you look at who heads the health committees and the others in Congress, related committees in Congress, their campaign contributors come from the pharmaceutical and drug industry.
So you have the governments representing their campaign contributors, the military and state department desks at the Senate and House are subsidized and paid for by the military industrial complex, the health departments from the drug companies, and so on and so forth.
So we're that part of the problem of what has made America a failed economy. And it's a failed economy because of the austerity that this debt apartheid has created.
RADHIKA DESAI: And we should probably soon shift to talking about solutions. But let me just add a small point to what you were saying, which is that, of course, if you look at the US economy today, you will see that over the neoliberal period, what has happened is that it has become dominated, of course, by the financial sector, the so-called FIRE sector, finance, insurance, and real estate.
And on top of that, if you look at what are the other sectors of the US economy, which are really important and lucrative, you will see that they are the military industrial complex, they are the big pharma, and they are information and communications technology.
And in pretty well all of these cases, these sectors are characterized by a high degree of monopoly, a high degree of rent-seeking in the sense that a military industrial complex, for example, essentially relies on vast government contracts, which are risk-free in which they get to mark up costs as much as they like.
And big pharma and information and communications technology rely on intellectual property rights in order to secure their monopoly.
So in all of these ways, this has created an economy which is very undynamic, it is not very efficient, but at the same time, it is very lucrative for those who own it, which of course puts an added burden on ordinary Americans.
MICHAEL HUDSON: Well, one of the problems of it being undynamic is you're having a decline in office space, in commercial real estate. We've been talking about homeownership rates and how unfair that is, but you remember back in 2008 when there was the property price crash, you had what was called "jingle mail".
You would have buyers, especially in Nevada and Florida, where there was a huge run-up in housing prices, they'd say, okay, I owe $500,000 for this house, but now the house just like it next door is selling for $300,000. I'll just mail back the keys to the bank and say, okay, I'm defaulting, you can have the house, I'm just not going to pay, I'm going to take out a new loan and buy the house next door.
Well, that phenomenon is now happening for businesses. Apparently [only] 40% of the US commercial properties are occupied. In other words, since COVID, and most of all, since the economy began to shrink as a result of this debt deflation, businesses have been going out of business.
Even those who are in business, you have people working from home. Now, if you have the average occupancy rate of buildings being only 40%, how is the owner going to have the money to pay for the bank?
Well, because the banks have lent almost 100% of the value of the building to the homeowner who's willing to pay all of the rents as interest, rent is for paying interest, that's the basic motto.
What they want is the capital gain in the price of the building. They realize they're not going to be a capital gain. This was all fictitious capital, it's going down, we're mailing our keys back to the bank and we're walking away from the building.
This year and next year, there is such an enormous trillions of dollars of commercial real estate falling due, not only here, but in England and other countries, that the banks are all of a sudden going to be left with mortgages that are unpaid.
Against these mortgages, they have liabilities to their depositors, to their bondholders, and most of all, they want to pay millions of dollars to the, I think Jamie Dimon, the head of Chase Manhattan, gets $29 million a year for running a company that's gone bankrupt and is kept alive because he gives some of that $29 million to the politicians who continue to appoint Federal Reserve people who will bail them out. That's what you call a circular flow.
What are you going to do when all of a sudden the banks should be going under? Well, normally, if they've made a bad loan, somebody has to suffer. Who's going to suffer?
As Bill Clinton said when he was told you have to do what Alan Greenspan says and support the banks, Clinton said, oh, it's all about the bondholders.
In 2009, when Obama came in and decided to bail out the banks, Sheila Bair, the head of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, said, wait a minute, we have a crooked, incompetent bank. There's one bank in America that's more crooked than all the others and more incompetent. That's First National City Bank. Let's take it over. Let's make it a public bank. You can't let this bank destroy the whole economy by being so greedy that it makes loans way in excess of the value of property and keeps expecting to be bailed out so it can make more interest and pay its officers more. Let's drive it under.
And Obama and his Treasury secretary, Tim [Geithner], said it's all about the bondholders who own the bank.
So the question is, what will the banks do when all these mortgage loans go under? Well, wipe out the stockholders.
But the bondholders are the wealthiest 1% of the population. They're the ones who own most of the bank bonds.
Who do you think the government is going to support? Is it going to support the economy or the stockholders or the 1%?
That really is the way in which you should think about an economy being an apartheid economy, not simply ethnically and racially, but financially. That's the real apartheid between creditors and debtors that I think all of our shows are examining from different perspectives.
RADHIKA DESAI: Well, I'd just like to add a couple of points to what you were saying, Michael. This is very interesting because if you look at commercial real estate, there's no doubt for the last many months there have been headlines about how there is a collapse of commercial real estate prices. It's coming. In fact, it's already happening.
As Michael says, the fall in the value of commercial real estate is already ongoing from what we read in the financial press. The really big prestige buildings may not be affected, but the next layer and down, all these buildings will be affected.
Everybody who has walked around a big city in North America or for that matter elsewhere in Europe will see that commercial space is essentially going down. So many are boarded up. So many are empty and so on.
And according to one measure, about 10% of US bank assets actually rely on the value of commercial real estate. Now, Michael asks, you know, when the crisis comes, well, the crisis is already here.
So who is the Federal Reserve going to help? But you know what, I'm not even sure. And the US government, who are they going to help? Who are US authorities going to help?
I'm not even sure they're going to be able to help them because the fact is that as the value of these assets decline, banks already have to report them if they are publicly listed on an ongoing basis, which means that their shares will already go down.
And there is no doubt that a crash will come. And when it comes, yes, the Federal Reserve will once again, as you saw with the Silicon Valley Bank, essentially, in fact, there was another point that I wanted to make there. Essentially, Ms. [Janet] Yellen stepped forward and said, we are going to guarantee all depositors, even if their deposits are higher than $250,000.
Now, you might think that this is somehow a very democratic thing. But on the contrary, if you look at what kind of bank Silicon Valley Bank was, essentially, it was like a club in which a select group of rich people who are all connected with one another lent each other vast quantities of money.
Now, what does lending mean? It means that I go to my friend and, you know, Silicon Valley Bank and say, you know, please give me $5 million. I'm going to have a startup. You don't even look at whether my startup is worth supporting. You just say, okay, I'll give you, I'm going to show a deposit of $5 million in your account. These are the deposits that Ms. Yellen was protecting.
This is not even the money that they have deposited in the bank. This is money that is in a deposit in my name because it has been lent to me.
So, if you think about just how huge is the boondoggle that is protecting the interests of the tiny minority of the very wealthy, I hope in this program we've given you some idea of the lengths to which US authorities have gone to protect the wealth of this minority.
And in our next show, maybe what we'll do is we are going to devote it entirely to talking about what needs to happen if we are going to move away from this kind of economy.
MICHAEL HUDSON: That's a good way to end it. There's so much that it's leading into. And the last thing that the Federal Reserve wants is for—what if banks reported the actual market value of their assets?
When you have a balance sheet, assets and liabilities, they're holding the assets at the price that they made the loan for, say $100 million for a building. But what if they reported their assets as only $40 million for the building? You would have bank assets here and the liabilities here. They'd look just like most people in America.
50% of Americans don't have any assets, but they have a big debt. That's an interesting bar chart to show, assets, liabilities. And you can look at it by income group.
The Federal Reserve does not produce believable statistics on debt as a proportion of income.
If you look at the Federal Reserve statistics of debt to income by percentile, 10%, 20%, nothing has changed in the last 50 years. Nobody's run into debt at all. Because they say, let's assume that debt is constant for the last half century. The statistics are fictitious.
And they're fictitious because that protects the fact that most of this, what passes as bank capital is fictitious. I mean, we're in a fictitious economy.
It's sort of like trying to read about international affairs in the New York Times. That's about as realistic as the Federal Reserve statistics are.
RADHIKA DESAI: Exactly. I mean, it's basically the rich people of the United States and the big financial institutions of the U.S. are in a situation in which, you know, they make a bad investment, they make a loss and they go, oops.
And then the Federal Reserve, which is their sugar daddy, essentially comes and makes good all their losses. It gives them more money to plug the holes in their balance sheets that they have themselves created out of their own greed and misjudgment and bad judgment.
So there we have it. It's this kind of economy that, unfortunately, the United States is laden down with today. And so the question naturally arises, what kind of economy do Americans need in its place?
MICHAEL HUDSON: I want to add one point out there. The important thing is that these rich people who are not paying their debts do not have to pay penalty rates. The large businessmen who owe debts don't pay penalty rates.
You know that if you're a family and you're running a credit card debt, if you miss a payment in your electric bill or anywhere, your rate goes up from 19 percent to 30 percent or more.
That's not the case if you're rich people. There's one set of interest rates and penalties for 99 percent of the population, another set for the wealthiest 1 to 10 percent of the population, and you're not in it.
RADHIKA DESAI: And that's what we call financial apartheid. So I think with that, Michael and I will say goodbye and hope to see you in a couple of weeks and we'll talk about what kind of economy we need instead.
Thanks very much for joining us, and see you in a couple of weeks. Bye bye.





Best show yet!